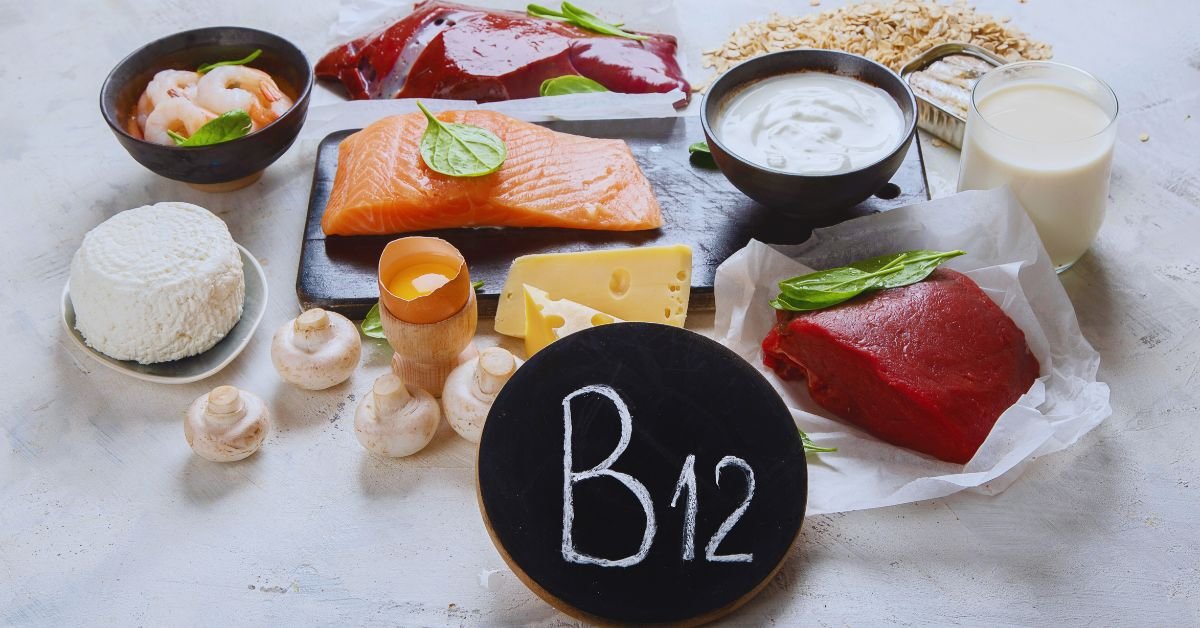
Are you feeling tired, weak, or experiencing tingling sensations in your hands and feet? It could be a sign of Vitamin B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. In this article, we will explore the importance of Vitamin B12, its sources, deficiency symptoms, and ways to maintain adequate levels for optimal health.
1. What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that belongs to the B-complex family. It is essential for the formation of red blood cells, DNA synthesis, and proper functioning of the nervous system. Unlike other vitamins, Vitamin B12 is not produced by plants or animals, but by microorganisms found in soil and water.
2. Importance of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is involved in numerous processes that are vital for overall health and well-being. It helps in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. It also supports the maintenance of a healthy nervous system and plays a crucial role in cognitive function.
3. Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Shellfish, such as clams and mussels, are particularly rich sources of Vitamin B12. For vegetarians and vegans, plant-based foods fortified with Vitamin B12, such as fortified cereals and nutritional yeast, can be an option.
4. Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Shellfish, such as clams and mussels, are particularly rich sources of Vitamin B12. For vegetarians and vegans, plant-based foods fortified with Vitamin B12, such as fortified cereals and nutritional yeast, can be an option.
5. Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can occur due to various reasons, including inadequate dietary intake, poor absorption, or certain medical conditions. Vegans, vegetarians, and older adults are at a higher risk of developing Vitamin B12 deficiency.
6. Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
The symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency can vary from mild to severe. Fatigue, weakness, and light headedness are common early signs. Over time, deficiency can lead to more serious complications, including anaemia, nerve damage, and mood disorders.
7. Risks and Complications of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Untreated Vitamin B12 deficiency can have significant consequences on overall health. It can lead to pernicious anaemia, a condition characterised by low red blood cell production. Long-term deficiency can also affect the nervous system, causing tingling sensations, numbness, and difficulty with coordination.
8. Diagnosing Vitamin B12 Deficiency
If you suspect a Vitamin B12 deficiency, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can conduct a blood test to measure your Vitamin B12 levels. In some cases, additional tests may be required to determine the underlying cause of deficiency.
9. Treating Vitamin B12 Deficiency
The treatment for Vitamin B12 deficiency typically involves Vitamin B12 supplementation. Depending on the severity of the deficiency, oral or injectable supplements may be prescribed. In cases where absorption is an issue, high-dose supplements or regular injections may be necessary.
10. Vitamin B12 Supplements
Vitamin B12 supplements are available over-the-counter and in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and sublingual sprays. It is important to choose a reputable brand and follow the recommended dosage. Regular intake of supplements can help maintain optimal Vitamin B12 levels.
11. Dietary Tips for Increasing Vitamin B12 Intake
In addition to supplements, a well-balanced diet can contribute to adequate Vitamin B12 intake. Including animal-based foods such as lean meats, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products can help meet your requirements. For vegetarians and vegans, fortified plant-based products and nutritional yeast can be beneficial.
12. Vegan and Vegetarian Sources of Vitamin B12
Vegans and vegetarians can face challenges in obtaining sufficient Vitamin B12 from their diet alone. However, there are options available. Fortified plant-based milk, breakfast cereals, and meat substitutes can provide a source of Vitamin B12. Nutritional yeast is another popular choice that can be sprinkled over various dishes.
13. Vitamin B12 and Brain Health
Emerging research suggests that Vitamin B12 may play a role in brain health and cognitive function. Adequate levels of Vitamin B12 are associated with a reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline and certain neurological conditions. However, more research is needed to fully understand the connection.
14. Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. Maintaining adequate levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. A balanced diet, including animal-based foods or fortified plant-based alternatives, along with appropriate supplementation, can help ensure optimal Vitamin B12 levels. If you suspect a deficiency, consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Learn How it Works!
Can I get enough Vitamin B12 from plant-based sources alone?
While plant-based sources of Vitamin B12 can be helpful for vegetarians and vegans, it can be challenging to obtain sufficient amounts from diet alone. Fortified products and supplements are recommended to meet the requirements.
Can Vitamin B12 deficiency be reversed?
In most cases, Vitamin B12 deficiency can be easily treated and reversed with appropriate supplementation. Regular intake of Vitamin B12 supplements can help restore optimal levels.
Is Vitamin B12 deficiency common?
Vitamin B12 deficiency is more common than you might think, especially among certain populations such as older adults, vegetarians, and vegans. Regular testing and monitoring can help detect and address deficiencies early on.
What are the long-term risks of untreated Vitamin B12 deficiency?
Untreated Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to serious complications such as anaemia, nerve damage, and neurological disorders. It is important to seek diagnosis and treatment to prevent long-term consequences.
Are there any side effects of Vitamin B12 supplementation?
Vitamin B12 supplementation is generally safe and well-tolerated. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as nausea, diarrhoea, or allergic reactions. If you have concerns, consult with a healthcare professional.