CoQ10, also known as coenzyme Q10 or ubiquinone, is a naturally occurring compound that plays a crucial role in the production of energy within our cells. This vital substance is not only an energy booster but also a powerful antioxidant, supporting various aspects of our health. In this article, we will explore the many benefits of CoQ10, its food sources, supplementation, and its impact on different aspects of our well-being.
1. What is CoQ10?
CoQ10 is a fat-soluble substance found in every cell of our body, particularly in the mitochondria, which are responsible for generating energy and majorly CoQ10 is produced there. It acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule that provides energy for cellular processes. CoQ10 exists in two forms: ubiquinone, the oxidised form, and ubiquinol, the reduced form. Both forms are essential for optimal cellular function.
2. Benefits of CoQ10
Supporting Energy Production
As a vital component in the electron transport chain, CoQ10 plays a key role in the production of ATP, the primary source of energy in our cells. By enhancing cellular energy production, CoQ10 can help combat fatigue, improve exercise performance, and support overall vitality.
Antioxidant Properties
CoQ10 acts as a potent antioxidant, neutralising harmful free radicals and protecting our cells from oxidative damage. This antioxidant activity contributes to the maintenance of healthy cells and tissues, and it also helps in reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Heart Health Support
The heart is one of the most energy-demanding organs in our body. CoQ10 is naturally present in high concentrations in heart muscle cells, where it aids in energy production and supports cardiovascular health. CoQ10 has been shown to help maintain healthy blood pressure, promote optimal heart function, and reduce the risk of certain heart conditions.
Cognitive Function Support
CoQ10 plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain function. It assists in the production of ATP in brain cells, which are highly metabolically active. Studies have suggested that CoQ10 supplementation may improve cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health, making it potentially beneficial for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
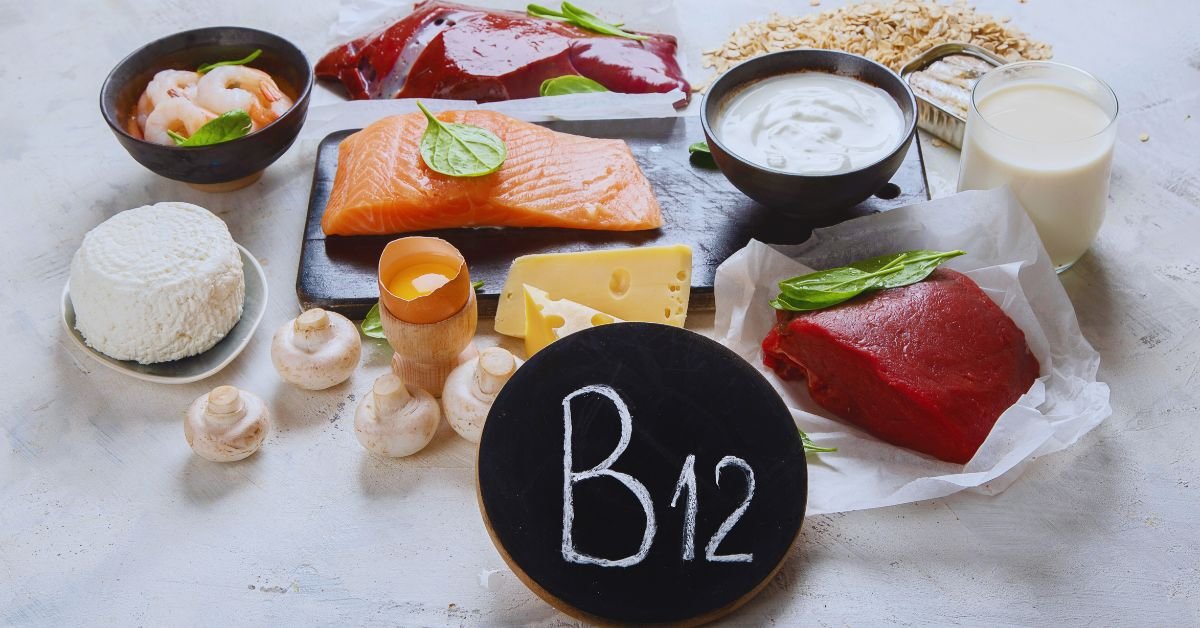
3. Food Sources of CoQ10
While our bodies naturally produce CoQ10, we can also obtain it from certain dietary sources. Foods rich in CoQ10 include organ meats (such as liver and heart), fatty fish (such as salmon and sardines), whole grains, nuts, and seeds. However, it’s important to note that the amount of CoQ10 obtained through diet alone may not be sufficient for optimal levels, especially as we age.
4. CoQ10 Supplementation
To ensure an adequate intake of CoQ10, many people turn to supplementation. When choosing a CoQ10 supplement, it’s important to consider the form, dosage, and potential side effects.
Choosing the Right Form
CoQ10 supplements are available in two main forms: ubiquinone and ubiquinol. Ubiquinone is the oxidised form, while ubiquinol is the reduced form. Both forms are effective, but ubiquinol is considered more bioavailable, especially for individuals over the age of 40 or those with certain health conditions.
Recommended Dosage
The optimal dosage of CoQ10 varies depending on individual needs and health conditions. For general health support, a daily dosage of 100-300 mg is commonly recommended. However, higher dosages may be required for specific health concerns, such as cardiovascular issues or neurological conditions. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalised advice.
Potential Side Effects
CoQ10 is generally safe and well-tolerated, with minimal side effects reported. However, some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, diarrhoea, or stomach upset. CoQ10 may also interact with certain medications, so it’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about any supplements you are taking.
5. CoQ10 and Aging
As we age, our body’s natural production of CoQ10 declines. This decrease in CoQ10 levels may contribute to age-related health issues and decreased energy levels. Supplementation with CoQ10 can help replenish these declining levels, providing support for overall well-being and healthy ageing.6. CoQ10 and Statin Use
Statin medications, commonly prescribed for managing high cholesterol, can deplete CoQ10 levels in the body. This depletion may lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and other adverse effects. Supplementing with CoQ10 can help counterbalance the statin-induced deficiency and reduce the risk of associated side effects.7. CoQ10 and Exercise Performance
CoQ10 supplementation has shown potential benefits for exercise performance. By increasing cellular energy production, CoQ10 can enhance endurance, reduce fatigue, and support post-workout recovery. Athletes and individuals engaged in regular physical activity may consider incorporating CoQ10 into their supplement regimen for optimal performance.8. CoQ10 and Fertility
CoQ10 plays a crucial role in the reproductive system, particularly in egg and sperm health. As women age, the quantity and quality of eggs decline, which can affect fertility. CoQ10 supplementation has shown promising results in improving egg quality and supporting healthy ovarian function. Men can also benefit from CoQ10 supplementation, as it may enhance sperm quality and motility.9. CoQ10 and Migraines
Migraines are severe headaches that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. CoQ10 has shown potential in reducing the frequency and severity of migraines. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may help alleviate migraine symptoms by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain.10. CoQ10 and Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterised by high blood sugar levels. CoQ10 supplementation has been studied for its potential benefits in diabetes management. It may help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce oxidative stress, and support overall metabolic health. However, further research is needed to establish its precise role in diabetes treatment.11. CoQ10 and Cancer
CoQ10’s antioxidant properties make it an intriguing subject of cancer research. While studies are ongoing, preliminary evidence suggests that CoQ10 supplementation may enhance the effectiveness of conventional cancer treatments and provide additional benefits, such as reducing chemotherapy-induced side effects. It is important to note that CoQ10 should not be used as a standalone cancer treatment.12. CoQ10 and Skincare
CoQ10’s antioxidant and energy-boosting properties extend to skincare as well. It helps protect the skin from oxidative damage, promotes collagen synthesis, and supports skin cell rejuvenation. Incorporating CoQ10 into skincare products or using CoQ10 supplements can contribute to a healthy, youthful complexion.13. CoQ10 and Mitochondrial Disorders
Mitochondrial disorders are a group of genetic disorders that affect the function of mitochondria. CoQ10 supplementation has shown promise in improving mitochondrial function and reducing symptoms associated with these disorders. It can enhance energy production and potentially slow down disease progression, although individual responses may vary.Summary
CoQ10, a vital compound involved in cellular energy production, offers a wide range of benefits for overall health and well-being. From supporting energy levels and heart health to promoting cognitive function and skincare, CoQ10’s impact reaches far and wide. While it can be obtained from certain foods, supplementation can ensure adequate levels, especially as we age or face specific health challenges. As always, consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the most appropriate approach for your individual needs.Frequently Asked Questions
Learn How it Works!
Is CoQ10 safe to take long-term?
CoQ10 is generally safe for long-term use, but it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalised guidance.
Can CoQ10 interact with medications?
CoQ10 may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and chemotherapy drugs. Consult with your doctor or pharmacist to check for any potential interactions.
Can CoQ10 help with weight loss?
CoQ10 is not directly linked to weight loss. However, by supporting cellular energy production, it can indirectly contribute to maintaining an active lifestyle, which is crucial for weight management.
Can CoQ10 improve fertility in men and women?
CoQ10 supplementation has shown potential benefits for both female and male fertility by improving egg and sperm quality. However, individual results may vary, and it’s important to consult with a fertility specialist for personalised advice.
Is CoQ10 suitable for vegetarians and vegans?
CoQ10 is naturally found in animal-based products. However, vegetarian and vegan-friendly CoQ10 supplements derived from microbial fermentation are available, making it suitable for individuals following these dietary lifestyles.
Which one is better: ubiquinone or ubiquinol ?
Ubiquinone supplements are widely available, affordable and can effectively increase CoQ10 levels in the body. They are suitable for most individuals, especially those under the age of 40 or without specific health conditions.On the other hand, ubiquinol supplements offer enhanced bioavailability, making them a preferred choice for individuals over the age of 40 or those with conditions that may impair the body’s ability to convert ubiquinone to ubiquinol. One should note that ubiquinol form of CoQ10 is readily available to support various biological functions.