Astaxanthin: The Comprehensive to Nature’s Super Antioxidant The Red Miracle.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. What is Astaxanthin?
3. How Does Astaxanthin Work?
4. The Health Benefits of Astaxanthin
– 4.1 Promotes Joint and Muscle Health
– 4.2 Supports Eye Health
– 4.3 Enhances Skin Health
– 4.4 Boosts Immune Function
– 4.5 Reduces Inflammation
– 4.6 Supports Cardiovascular Health
– 4.7 Enhances Cognitive Function
– 4.8 Protects Against UV Damage
– 4.9 Aids in Exercise Performance and Recovery
– 4.10 Supports Anti-Aging
– 4.11 Improves Male Fertility
– 4.12 Assists in Managing Diabetes
– 4.13 Supports Liver Health
– 4.14 Alleviates Symptoms of Asthma
– 4.15 Enhances Overall Well-being
5. How to Incorporate Astaxanthin into Your Daily Routine
– 5.1 Dietary Sources of Astaxanthin
– 5.2 Supplements
– 5.3 Topical Applications
6. Potential Side Effects and Precautions
7. Conclusion
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
– 8.1 Is astaxanthin safe for everyone to consume?
– 8.2 Can astaxanthin replace sunscreen for sun protection?
– 8.3 How long does it take to experience the benefits of astaxanthin?
– 8.4 Can astaxanthin improve athletic performance?
– 8.5 Is astaxanthin suitable for vegetarians and vegans?
1. Introduction
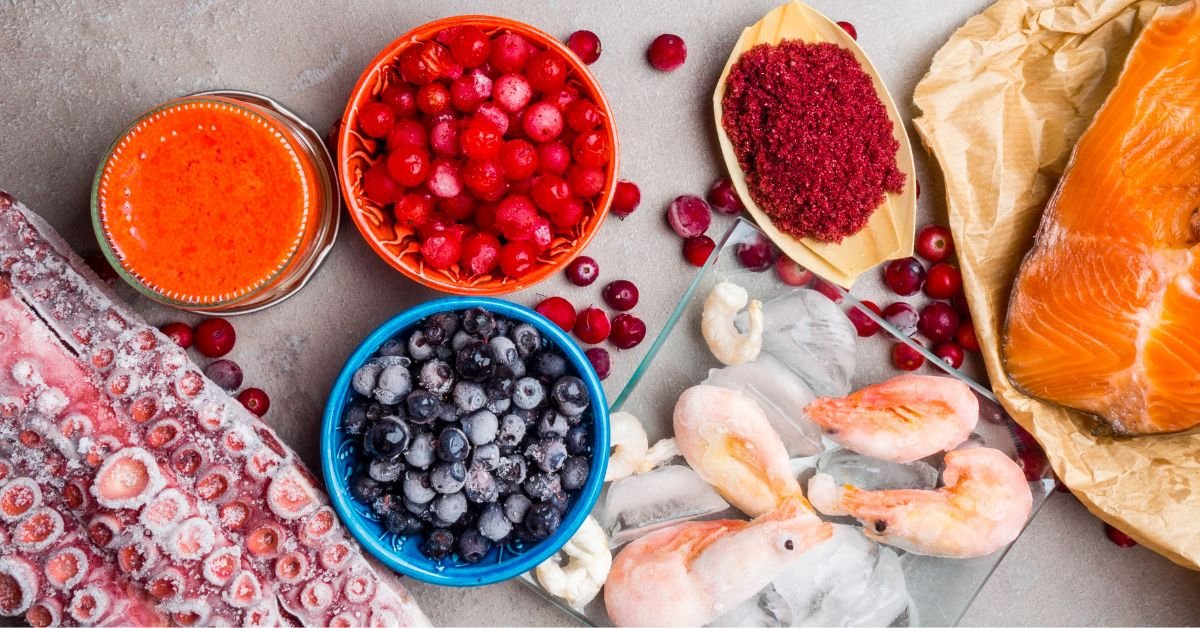
In the realm of natural antioxidants, astaxanthin stands out as a powerhouse that offers numerous health benefits. This vibrant red pigment is found in various marine organisms, including microalgae, salmon, shrimp, and krill. In recent years, it has gained significant attention for its exceptional antioxidant properties and its potential to support overall well-being. This article explores the fascinating world of astaxanthin, shedding light on its functions, health benefits, sources, and more.2. What is Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin belongs to a group of compounds known as carotenoids, which are responsible for the vivid colours of plants and animals. It is produced by microalgae called Haematococcus pluvialis as a protective mechanism against harsh environmental conditions, such as intense sunlight and nutrient deprivation. When marine organisms consume these algae, they accumulate astaxanthin in their tissues, giving them their distinct reddish hue.3. How Does Astaxanthin Work?
Astaxanthin’s exceptional antioxidant properties are attributed to its unique molecular structure. It has the ability to neutralise free radicals, highly reactive molecules that can cause cellular damage and oxidative stress. Unlike many other antioxidants, astaxanthin is highly versatile and can protect both the inner and outer layers of cells, including the cell membrane and the mitochondria.4. The Health Benefits of Astaxanthin
4.1 Promotes Joint and Muscle HealthAstaxanthin has shown promising effects in promoting joint and muscle health. Its potent anti-inflammatory properties help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the joints, potentially alleviating symptoms associated with conditions such as arthritis. Moreover, astaxanthin may support muscle recovery and reduce exercise-induced muscle damage, making it beneficial for athletes and active individuals.4.2 Supports Eye HealthThe eyes are highly susceptible to oxidative damage due to their exposure to light and environmental factors. Astaxanthin, with its powerful antioxidant properties, has been found to support eye health by protecting against oxidative stress, reducing eye fatigue, and supporting visual acuity. It may also help prevent age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of vision loss in older adults.4.3 Enhances Skin Health
Astaxanthin’s ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce inflammation makes it a valuable ingredient for promoting skin health. It can help protect the skin from UV-induced damage, minimise wrinkles and fine lines, improve skin elasticity, and enhance overall skin appearance. Additionally, astaxanthin may aid in managing certain skin conditions, such as acne and rosacea, by reducing inflammation and promoting skin healing.
4.4 Boosts Immune Function
A strong immune system is essential for overall health and well-being. Astaxanthin has been found to enhance immune function by modulating the activity of immune cells and reducing inflammation. By supporting the immune system, it helps the body defend against pathogens and maintain optimal health.
4.5 Reduces Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a common underlying factor in various chronic diseases. Astaxanthin’s potent anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce inflammation throughout the body, potentially benefiting individuals with conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
4.6 Supports Cardiovascular Health
Astaxanthin has been shown to promote cardiovascular health by reducing oxidative stress, improving blood lipid profiles, supporting blood vessel function, and reducing inflammation. These effects may contribute to a lower risk of heart disease and related complications.
4.7 Enhances Cognitive Function
As we age, cognitive decline becomes a concern for many individuals. Astaxanthin shows promise in supporting brain health and cognitive function. It can cross the blood-brain barrier and protect brain cells from oxidative damage, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases and age-related cognitive decline.
4.8 Protects Against UV Damage
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can damage the skin and increase the risk of skin cancer. Astaxanthin’s ability to quench free radicals and its anti-inflammatory properties make it an effective natural protector against UV-induced damage. While it should not replace sunscreen, astaxanthin can provide an additional layer of defence against harmful UV rays.
4.9 Aids in Exercise Performance and Recovery
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are constantly seeking ways to optimise their performance and enhance recovery. Astaxanthin has been studied for its potential benefits in these areas. It may improve endurance, increase muscle strength, reduce exercise-induced oxidative stress, and promote faster recovery following intense physical activity.
4.10 Supports Anti-Aging
Astaxanthin’s potent antioxidant properties make it a valuable tool in combating signs of ageing. By neutralising free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, it helps protect cells and tissues from damage, potentially reducing the appearance of wrinkles, age spots, and other age-related skin changes.
4.11 Improves Male Fertility
Male infertility can be attributed to various factors, including oxidative stress and inflammation. Astaxanthin has shown promise in improving sperm quality, count, and motility, potentially enhancing male fertility. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects contribute to a healthier reproductive system in men.
4.12 Assists in Managing Diabetes
Diabetes is a complex metabolic disorder characterised by high blood sugar levels. Astaxanthin may offer benefits for individuals with diabetes by reducing oxidative stress, improving insulin sensitivity, and decreasing inflammation. These effects can help manage blood sugar levels and potentially reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
4.13 Supports Liver Health
The liver plays a crucial role in detoxification and overall health. Astaxanthin has been found to support liver function by reducing inflammation, protecting against oxidative stress, and promoting liver cell regeneration. These properties make it a valuable nutrient for maintaining liver health and preventing liver damage.
4.14 Alleviates Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterised by inflammation and airway constriction. Astaxanthin’s anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce inflammation in the airways, potentially alleviating symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. While it should not replace prescribed asthma medications, astaxanthin may offer complementary support for individuals with asthma.
4.15 Enhances Overall Well-being
The cumulative benefits of astaxanthin contribute to overall well-being and vitality. By protecting cells, reducing inflammation, and supporting various bodily functions, astaxanthin helps optimise health and promotes a sense of vitality and wellness.
5. How to Incorporate Astaxanthin into Your Daily Routine
5.1 Dietary Sources of AstaxanthinAstaxanthin can be obtained through dietary sources, primarily seafood. Salmon, shrimp, crab, lobster, and trout are excellent sources of astaxanthin. Consuming a variety of seafood regularly can help increase your astaxanthin intake.5.2 SupplementsAstaxanthin supplements are also available in the form of capsules, softgels, or tablets. When choosing a supplement, opt for reputable brands that provide high-quality astaxanthin derived from natural sources. Follow the recommended dosage as indicated on the product label or consult with a healthcare professional for personalised guidance.5.3 Topical ApplicationsAstaxanthin is increasingly being incorporated into skincare products due to its potential benefits for skin health. Look for creams, serums, or oils that contain astaxanthin as an active ingredient to enjoy its antioxidant and anti-aging properties for your skin.6. Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Astaxanthin is generally considered safe for most individuals when taken at recommended dosages. However, in rare cases, it may cause mild side effects such as stomach discomfort or changes in stool colour. As with any supplement, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting astaxanthin, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking other medications.7. Conclusion
Astaxanthin, the powerful antioxidant derived from marine organisms, offers a wide array of health benefits. From supporting joint and muscle health to enhancing skin vitality, boosting immune function, and promoting cardiovascular well-being, astaxanthin proves to be a versatile nutrient with remarkable properties. Whether obtained through dietary sources or supplements, incorporating astaxanthin into your daily routine can contribute to improved overall health and well-being.Frequently Asked Questions
Learn How it Works!
Is astaxanthin safe for everyone to consume?
Astaxanthin is generally safe for most individuals when taken at recommended dosages. However, if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking medications, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting astaxanthin.
Can astaxanthin replace sunscreen for sun protection?
No, astaxanthin should not replace sunscreen. While it offers some protection against UV-induced damage, it’s essential to use sunscreen with an appropriate SPF for adequate sun protection.
How long does it take to experience the benefits of astaxanthin?
The time it takes to experience the benefits of astaxanthin can vary depending on individual factors. Some individuals may notice improvements within a few weeks, while others may require longer-term use for noticeable effects.
Can astaxanthin improve athletic performance?
Astaxanthin has been studied for its potential benefits in exercise performance and recovery. It may improve endurance, muscle strength, and recovery time following intense physical activity.
Is astaxanthin suitable for vegetarians and vegans?
Astaxanthin is primarily derived from seafood sources. However, vegetarian and vegan astaxanthin supplements derived from microalgae are available for individuals following plant-based diets.