Introduction:
Welcome to an intriguing journey into the world of telomeres! These tiny structures at the end of our chromosomes play a significant role in determining how our cells age and function. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the science, mechanisms, and potential impact of telomeres on our overall health and longevity.
Telomeres: The Guardians of Chromosomes
At the heart of every human cell lies a set of chromosomes carrying our genetic information. Telomeres are like the protective caps at the end of shoelaces, preventing the chromosomes from fraying and sticking to other chromosomes. They consist of repetitive DNA sequences and associated proteins that ensure the stability and integrity of our genetic material during cell division.Telomeres are structures made of DNA sequences and proteins found at the ends of chromosomes. They consist of repetitive DNA sequences that protect the ends of chromosomes from becoming frayed or tangled. Telomeres serve three major purposes: they help to organise each of our 46 chromosomes in the nucleus of our cells, they protect the ends of chromosomes from being mistaken for broken DNA, and they ensure that the DNA replication machinery can fully copy the DNA in each chromosome. Each time a cell divides, the telomeres become slightly shorter. Eventually, they become so short that the cell can no longer divide successfully, and the cell dies. Telomeres are critical for maintaining genomic integrity and may be factors for age-related diseases. Laboratory studies show that telomere dysfunction or shortening is commonly acquired due to the process of cellular ageing and tumour development. Telomerase is an enzyme that can rebuild telomeres to restore cell division6. However, if a cell keeps dividing uncontrollably and overcomes the limitations of telomeres, a cancerous tumour can form
How Telomeres Work: Unravelling the Mechanisms
Telomeres are dynamic structures that undergo changes throughout our lives. With each cell division, these protective caps shorten, eventually leading to cellular ageing and death. The enzyme telomerase can counteract this shortening process, extending the lifespan of certain cells. Learn more about the fascinating mechanisms behind telomeres and how they influence the ageing process.
The Telomere-Ageing Connection: What Science Tells Us
Scientific research has delved deep into understanding the link between telomeres and ageing. Studies have shown that telomere length can serve as a predictor of overall health and longevity. Learn about the findings from various research endeavours and how they have shaped our understanding of ageing and cellular health.
How do telomeres affect ageing ?
Telomeres play a central role in cell fate and ageing by adjusting the cellular response to stress and growth stimulation on the basis of previous cell divisions and DNA damage. Telomere length shortens with age, and progressive shortening of telomeres leads to senescence, apoptosis, or oncogenic transformation of somatic cells, affecting lifespan. Short telomeres are implicated in a variety of disorders including dyskeratosis congenita, aplastic anaemia, pulmonary fibrosis, and cancer. Telomere shortening is commonly regarded as an important contributor to organismal ageing. Among people older than 60, those with longer telomeres live an average of five years longer than those with shorter telomeres. This study suggests that lifespan could be increased by five years by increasing the length of telomeres in people with shorter ones. People with longer telomeres still experience telomere shortening as they age. 10 years and perhaps 30 years could be added to our lifespan by completely stopping telomere shortening . Therefore, telomeres affect ageing by shortening with age and contributing to senescence, apoptosis, or oncogenic transformation of somatic cells, which affects lifespan.
What are some factors that can accelerate telomere shortening?
Factors that can accelerate telomere shortening include:
- Smoking.
- Obesity.
- Lack of exercise.
- Consumption of unhealthy diet.
- Exposure to pesticides and pollution.
- Depression.
- Oxidative stress.
- Inflammation.
- Life stress.
These factors can cause accelerated telomere shortening, leading to senescence, apoptosis, or oncogenic transformation of somatic cells, which affects lifespan. Therefore, adopting a healthy lifestyle, reducing stress, and avoiding exposure to harmful environmental factors may help to slow down telomere shortening and promote healthy ageing.
Exercise and Telomeres: Moving Towards Youthful Cells
Regular physical activity not only benefits our cardiovascular health but also impacts telomere length. Studies have found a positive association between exercise and longer telomeres, suggesting that staying active can play a crucial role in healthy ageing.
How can stress affect telomere length
Stress can affect telomere length in several ways, as supported by the search results. Here are some of the key findings:
- Chronic stress tends to be associated with shorter telomeres16. UCLA researchers have confirmed that people subjected to chronic stress tend to have shorter telomeres.
- Perceived stress can also predict telomere length . One of the largest studies of telomere length found that stressful event exposure alone (not accounting for perceived stress) predicts telomere length1.
- Stress can cause oxidative stress, which can shorten telomeres2. In vitro, oxidative stress can shorten telomeres, and antioxidants can decelerate shortening.
- Chronic psychological stress can lead to disease through many pathways, and research from in vitro studies suggests that stress can shorten telomeres. Short telomeres confer risk of degenerative diseases.
- Women who perceive recent stress (less than a year) due to their own health condition, or for feeling prolonged stress (more than a year) related to the health issues of their parents or relatives, present a significant decrease in telomere length Unexpectedly, contrary to men, an increase in telomere length was observed among women who perceived stress from care for sick relatives with respect to those who did not report stress
In summary, stress can affect telomere length by causing oxidative stress, leading to disease, and shortening telomeres. Chronic stress and perceived stress are associated with shorter telomeres, and women who perceive stress due to their own or their relatives’ health issues may experience a decrease in telomere length.
Telomeres and Environmental Factors: Navigating the Modern World
Our modern environment exposes us to various pollutants and toxins that can impact telomere length and cellular function. From air pollution to exposure to chemicals, discover how these environmental factors can affect our telomeres and what we can do to mitigate their effects.
Telomeres and Sleep: Unwinding for Optimal Cellular Health
Quality sleep is essential for cellular repair and maintenance, including telomere preservation. Explore the science behind sleep and telomeres and learn practical tips for improving your sleep habits.
How Do We Increase Telomeres Length ?
Increasing telomere length is a topic of interest in the field of ageing and longevity. While it is generally believed that telomeres naturally shorten over time and cannot be lengthened, there are some strategies that may help maintain telomere length or slow down the rate of telomere shortening. Here are some approaches that have been suggested:
Dietary Changes:
- Increase dietary fibre: Some studies have hypothesised that an increased amount of dietary fibre could positively regulate telomere length
- Focus on a plant-rich diet: A plant-rich diet full of fibre, antioxidants, vitamins, and phytonutrients may result in longer telomeres5.
- Eat telomere-protective foods: Consuming foods high in vitamin C, polyphenols, and anthocyanins, such as red peppers, kale, dark chocolate, and blueberries, may help protect DNA and potentially maintain telomere length.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity and exercise can decrease oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, which may help protect telomeres from damage.
- Manage stress: Reducing or managing stress levels may have a positive impact on telomere length.
- Get enough sleep: Sufficient sleep is important for overall health and may also play a role in telomere maintenance.
- Quit smoking: Smoking has been associated with accelerated telomere shortening, so quitting smoking can help slow down the rate of telomere loss.
Supplements:
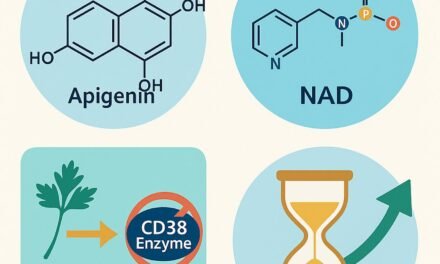
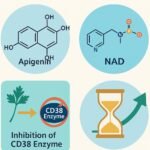
Vitamin D: Some studies have suggested that taking vitamin D supplements may increase telomere length, particularly in individuals with already short telomeres
It’s important to note that the research on telomere length and interventions to increase it is still ongoing, and the effectiveness of these strategies may vary among individuals. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or lifestyle.