Introduction to Pentadecanoic Acid:
Pentadecanoic acid, also known as C15:0, is a saturated fatty acid with a 15-carbon chain. It is classified as a medium-chain fatty acid (MCFA) and is naturally found in various foods. While it may not be as well-known as other fatty acids, pentadecanoic acid plays essential roles in human health and nutrition.
Chemical Structure and Properties:
Pentadecanoic acid has a straight-chain structure with 15 carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms and a carboxyl group at one end. Its molecular formula is CH3(CH2)13COOH. This fatty acid is solid at room temperature and is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and ether.
Natural Sources of Pentadecanoic Acid:
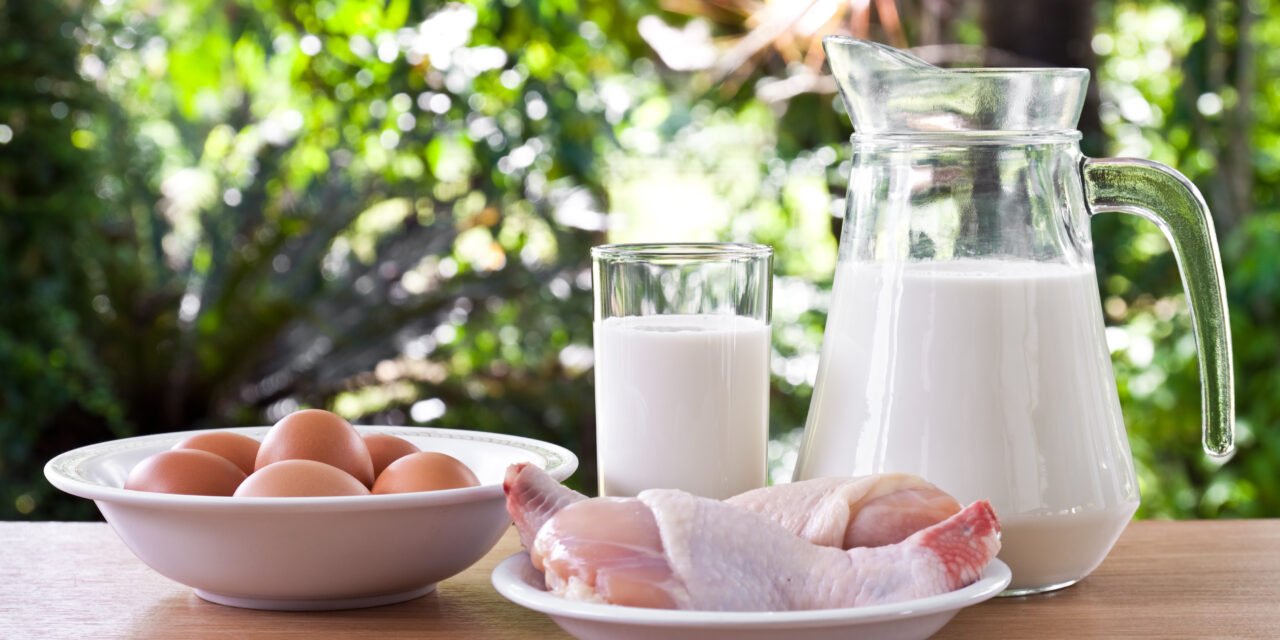
Pentadecanoic acid is found in small quantities in various foods, including dairy products such as milk and cheese, as well as certain meats. It is also present in some plant-based sources like whole grains and nuts, albeit in lower concentrations.
Health Benefits of Pentadecanoic Acid:
- Cardiovascular Health: Studies suggest that pentadecanoic acid may have beneficial effects on cardiovascular health. It has been linked to lower levels of LDL cholesterol, which is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease.
- Brain Function: Some research indicates that pentadecanoic acid may support cognitive function and brain health. It is believed to play a role in the structure and function of cell membranes in the brain.
Immune System Support: Pentadecanoic acid exhibits antimicrobial properties, potentially helping the body defend against harmful pathogens. It may contribute to a stronger immune system, although more research is needed to fully understand its effects. - Liver Health: Research indicates potential benefits for liver function.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Pentadecanoic acid might positively influence blood sugar levels
- Improving Energy Production: Pentadecanoic acid helps restore impaired mitochondrial function, enabling cells to produce the energy needed to maintain a healthy metabolism
- Enhancing Cellular Resilience: By incorporating sturdy C15:0 into cell membranes, pentadecanoic acid makes cells less fragile, promoting their longevity and functionality within the body’s metabolic processes.
- Restoring Communication Between Cells: Pentadecanoic acid naturally binds to receptors like PPARs alpha and delta, which play crucial roles in orchestrating metabolism, immunity, mood, appetite, and sleep. Activating these receptors helps in maintaining overall metabolic and immune health.
- Longevity: Research suggests C15:0 activates AMPK and inhibits mTOR, two signalling pathways considered crucial for longevity. These pathways influence cellular metabolism, ageing and lifespan.
Role in Nutrition and Metabolism:
Pentadecanoic acid is metabolised differently than long-chain fatty acids, making it a unique component of the diet. It is rapidly absorbed and transported to the liver, where it can be used as a source of energy or converted into other compounds.
Potential Side Effects and Risks:
While pentadecanoic acid is generally considered safe when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet, excessive intake may lead to weight gain and other health issues associated with high-fat diets. Individuals with specific medical conditions or dietary restrictions should consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to their fat intake.
Pentadecanoic Acid in Medical Research:
Researchers are actively studying the potential therapeutic applications of pentadecanoic acid in various medical conditions, including metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and inflammation. Preliminary findings suggest promising avenues for further investigation.
Dietary Recommendations and Supplementation:
Currently, there are no established dietary recommendations specifically for pentadecanoic acid intake. However, consuming a diverse range of foods that contain healthy fats, including pentadecanoic acid, can contribute to overall health and well-being. Some individuals may choose to supplement their diet with medium-chain fatty acids, including pentadecanoic acid, although more research is needed to determine optimal dosages and potential benefits.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, pentadecanoic acid is a unique fatty acid with potential health benefits, particularly in cardiovascular health, brain function, and immune support. While more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications, including pentadecanoic acid-rich foods in a balanced diet may offer various health advantages.
FAQs:
- What foods contain pentadecanoic acid?
Pentadecanoic acid is found in dairy products, meats, whole grains, and nuts. - Is pentadecanoic acid safe to consume?
Yes, pentadecanoic acid is generally safe when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. - Can pentadecanoic acid supplements improve health?
While some studies suggest potential benefits, more research is needed to support the use of supplements. - What are the recommended daily intake levels for pentadecanoic acid?
There are currently no established dietary guidelines for pentadecanoic acid intake. - Are there any interactions between pentadecanoic acid and medications?
Specific interactions with medications have not been widely reported, but individuals should consult healthcare professionals if concerned.